Do you interested to know about diethyl ether? Is it dangerous or not? What are the uses and hazards of diethyl ether? Then keep reading this article, we will provide you the scientific knowledge about diethyl ether, and visits regularly mbbsbooks.com for more updates. It is an organic molecule that belongs to the ether family of chemicals and is the main ingredient in most anesthetics. C2H5OC2H5 is the chemical formula, with the oxygen atom connecting the two ethyl groups.
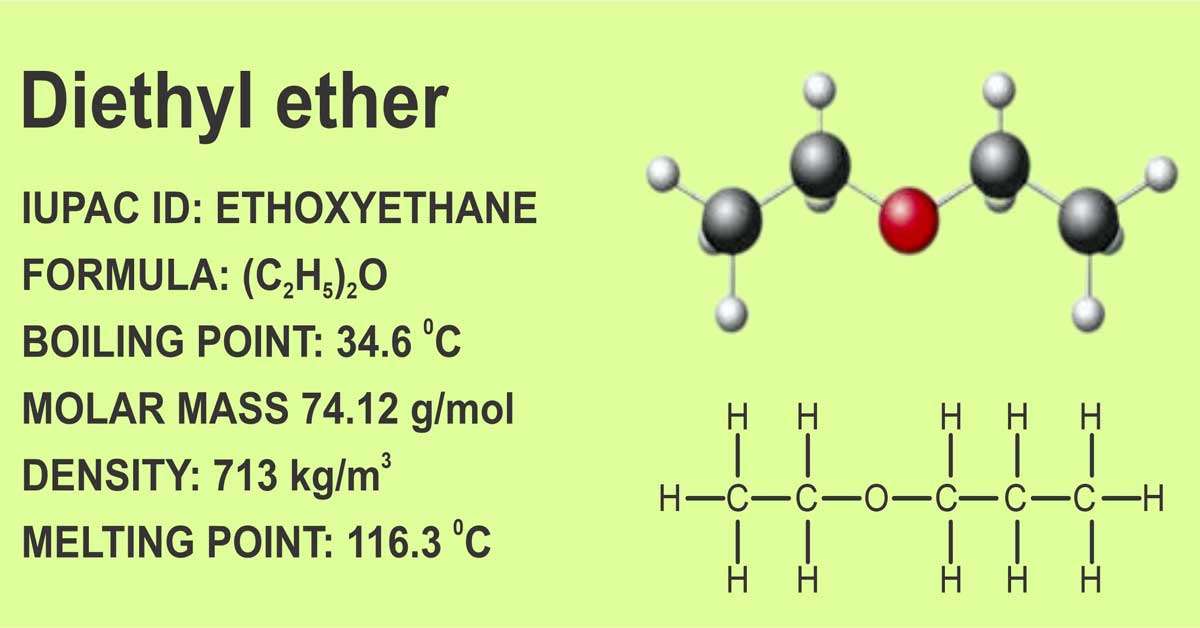
Diethyl ether structure
Ether is an organic compound comprising two carbon and one oxygen atom (C-O-C). Ether could be produced by condensing alcohol. Diethyl-ether, or ether, is a colorless, flammable, and volatile liquid with a long history as an anesthetic medication.
One oxygen atom is fused to two ethyl groups to form diethyl ether. It can be used as a cooling agent, a non-polar solvent, and an anesthetic inhalant. It is both an ether and a volatile chemical due to its low molecular weight and high volatility. It is also known by its IUPAC name, ethoxyethane.
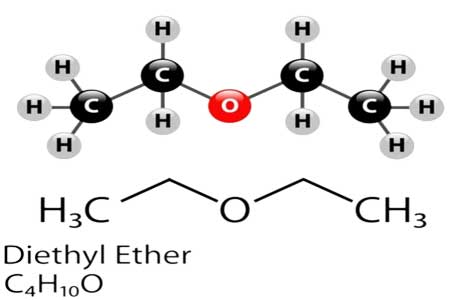
Diethyl ether synthesis
Ether is an organic compound comprising two carbon and one oxygen atom (C-O-C). Ether could be produced by condensing alcohol. Distilling ethyl alcohol with sulfuric acid yields ethyl ether. Pure ether (absolute ether) is required for medical applications and the production of Grignard reagents. It is obtained by cleaning crude ether with a saturated aqueous calcium chloride solution, followed by salt treatment.
It can be synthesized in laboratories and on a large scale using acid ether synthesis. Ethanol is combined with a strong acid, most commonly sulfuric acid (H2SO4). In water, the acid dissociates into H3O+ hydronium ions. A hydrogen ion protonates the electronegative oxygen atom in an ethanol molecule, giving the molecule a positive charge.
CH3CH2OH + H3O+ → CH3CH2OH+2 + H2O
This reaction must be carried out at temperatures lower than 150 °C to avoid the production of ethylene, an elimination product. Ethanol dehydrates into ethylene at higher temperatures. The reactants and products will eventually balance out if the process of making diethyl ether is reversed. To achieve a high ether yield while employing Le Chatelier’s principle, the ether must be distilled from the reaction mixture before it converts to ethanol.
The Williamson ether synthesis is another method for producing ethers. By dissolving an alkali metal in the alcohol to be used, an alkoxide is formed, which then nucleophilically substitutes for an alkyl halide.
Diethyl ether’s useful properties made it a popular choice as an anesthetic in various countries. In vivo, ether behaves similarly to alcohol and chloroform, except its heart-stimulating effects are stronger. Ether, a stimulant with rapid dispersal, is distinguished by rapid dissipation. The 1960s developed substitute chemicals.
Diethyl ether boiling point
Ethanol is a colorless, volatile, highly combustible liquid with a heated, sweetish flavor and a boiling point of 34.5 degrees Celsius (94.1 degrees Fahrenheit). It is slightly soluble in the water and has a lower density than water. As a result, it is buoyant and suitable for use in the ocean. The density of vapors is greater than that of air. It can be used as a solvent or in synthesizing other chemicals.
Diethyl ether is a solvent that is used in the production of many synthetic polymers and dyes. It is a common solvent for a wide range of substances such as bromine, iodine, the majority of fatty and resinous compounds, volatile oils, pure rubber, and various vegetable alkaloids.
Diethyl ether density
Diethyl ether has a molecular weight of 74.12 g/mol and is highly flammable and volatile. The density of diethyl ether is affected by both temperature and pressure. The density is approximately 0.71 g/cm3 at 25 degrees Celsius and 1 atmosphere and approximately 0.713 g/cm3 at 0 degrees Celsius and 1 atmosphere.
It’s critical to remember that the density of diethyl ether can change depending on how it’s measured. At -20 degrees Celsius and sea level pressure, the density is approximately 0.733 g/cm3, and at 40 degrees Celsius and sea level pressure, the density is approximately 0.685 g/cm3. Furthermore, the density of diethyl ether is affected by its purity because impurities can change its density. The density of an object can be precisely measured using high-purity diethyl ether.
Diethyl ether polarity
Because of its low dielectric constant, diethyl ether is classified as a non-polar solvent (4.33). Because the majority of organic compounds, including ethers, have a dipole moment, they are all polar. “polar” and “non-polar” describe solvents with high or low polarity. However, this is relative. Diethyl ether is near the bottom of the polarity scale, making it a non-polar substance. In the following section, the polar properties of Diethyl Ether are discussed in greater detail.
Uses for diethyl ether
Diethyl ether, also known as ethoxyethane or ethyl ether, has a variety of applications.
- Its primary application was as an anesthetic until safer alternatives became available after 1960.
- It is a solvent in various applications, including the hygiene, beauty, and pharmaceutical industries.
- Extraction: extracts organic molecules from plants, such as volatile oils and nitrogenous substances like alkaloids, steroids, phenols, and flavonoids.
- It is a precursor in synthesizing several other chemicals, including acetic acid and ethylene.
- It is a useful reagent because it is widely used in laboratories as a solvent, extraction agent, and reaction medium.
- Sixth, it is a fuel that can be used in internal combustion engines. Concerns about potential dangers limit its use.
- It was originally used as a refrigerant, but safer and more effective alternatives are now available.
- It is used as a solvent and reactant in various chemical synthesis processes. This method can synthesize various chemical compounds, including alcohols, ethers, and esters.
- Diethyl ethanol is used as a fixative and solvent in the perfume and fragrance industries and to extract plant essential oils.
- It is used as an insecticide and fumigant to eliminate insects and other pests from stored grains and seeds.
- It is a precursor in manufacturing explosives such as diethyl ether peroxide.
- It is safe to use as a cleaning agent on electrical equipment and other sensitive surfaces.
- It’s a solvent used to produce polymers like cellulose acetic acid.
- It is used in histology labs as a clearing agent to make biological tissues visible under the microscope.
Diethyl ether hazards
Because of its high flammability and volatility, it is a hazardous liquid. Diethyl ether poses the following risks:
- Highly combustible; it burns easily and produces an explosive mixture when mixed with air at room temperature, which can ignite flames, heat, or sparks.
- Explosive reactions: They can form explosive peroxides when exposed to light or air after being stored for a long time. Certain peroxides can cause a rapid and powerful explosion.
- Third, because this liquid burns so easily, there is a fire risk; fires involving it are notoriously difficult to extinguish. Water is dangerous and can spread a diethyl ether fire, so it should not be used to extinguish such blazes.
- Environmental risks: If not properly controlled, it can contaminate groundwater and surface water and endanger marine life.
- It’s bad for your health because it irritates your eyes, skin, and lungs. If breathed in or ingested, it can cause headaches, nausea, dizziness, and even unconsciousness. Diethyl ether intoxication can cause long-term kidney and liver damage.
- Your skin will have no trouble absorbing it. In skin contact, the substance must be removed immediately with soap and water.
- Toxicity; inhaling or ingesting large quantities may result in respiratory collapse and death.
- Incompatibility: It is incompatible with many substances, including strong oxidizing agents, acids, and alkalis. Dangerous reactions can occur when two different chemicals or substances come into contact with one another, such as releasing toxic fumes or starting a fire or explosion.
- Causes damage during transportation; classified as a hazardous item for shipping. It must be clearly labeled, packaged, and transported safely by road, rail, or air.
When working with or around diethyl ether, you must always take the necessary precautions, such as wearing gloves and eye protection. If you come into contact with diethyl ether, you should seek medical attention. It must be kept cold, dry, and well-ventilated, away from water.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does diethyl ether dissolve?
Diethyl ether, like other ethers, can dissolve a wide range of polar and non-polar chemical substances. Because ethers lack the hydrogen bonding network alcohols require to dissolve the solute, diethyl ether is frequently more effective at dissolving non-polar compounds.
Is diethyl ether the same as ether?
Diethyl ether, also known as anesthetic ether, is an organic compound that belongs to the ether family of chemicals. Its chemical formula, C2H5OC2H5, comprises two ethyl groups and one oxygen atom.
What happens if you inhale diethyl ether?
Inhaling diethyl ether can cause respiratory tract irritation. Drowsiness, arousal, nausea, vomiting, irregular breathing, and salivation can result from inhaling diethyl ether. Excessive exposure may result in coma or death.
Is ether still used to treat pain?
Ether is still widely used as an anesthetic in many developing countries due to its low cost, high therapeutic index, and lack of cardiac and respiratory side effects. Most developing countries have banned its use due to its high combustibility.