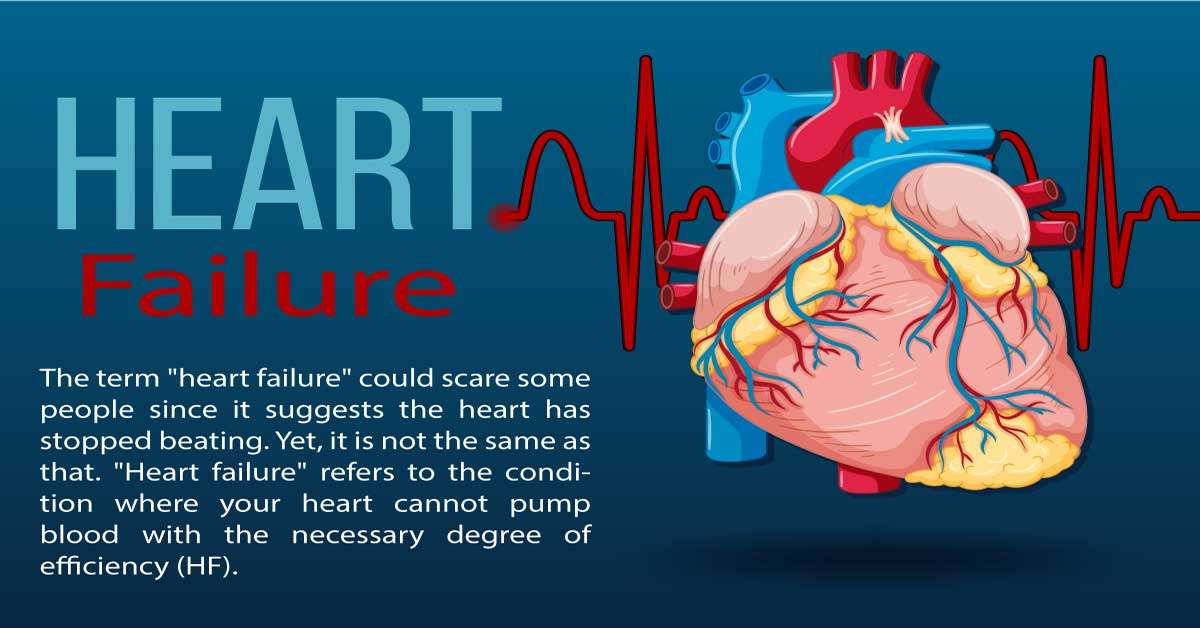
Do you interested to know about heart failure? Is it scary or not? With heart failure, you may live a healthy life or not. Here is a “Heart Failure Brochure” for you for your healthy life. We will provide answers to all questions in this blog post. The term “heart failure” could scare some people since it suggests the heart has stopped beating. Yet, it is not the same as that. “Heart failure” refers to the condition where your heart cannot pump blood with the necessary degree of efficiency (HF). Your body will receive less oxygen due to decreased pumping, which might make you feel weary and run down.
The heart is a hollow muscle the size of a human hand. It carries oxygenated-rich blood and nutrients throughout the body. The heart has four chambers: the upper atrium (atria) and the bottom ventricle (ventricle). The right side of the body gathers blood from the rest and pumps it to the lungs, enhancing the oxygen level. The left ventricle of the heart then distributes the blood throughout the body.
Another symptom of heart failure is an enlargement of the legs or lungs brought on by an abnormal fluid accumulation in those areas. This illness, known as edema, frequently results in a lack of breathability as a side effect. Heart failure is a very serious condition that requires continuous care from you and the medical personnel treating you.
The good news is that the condition may be managed with medication, a diet that contains less salt, and consistent physical activity. The heart failure brochure may be helpful to enlist the assistance of loved ones and friends who are familiar with your disease and the alterations to your lifestyle to aid you in forming new, healthy habits.
What is the function of the heart?
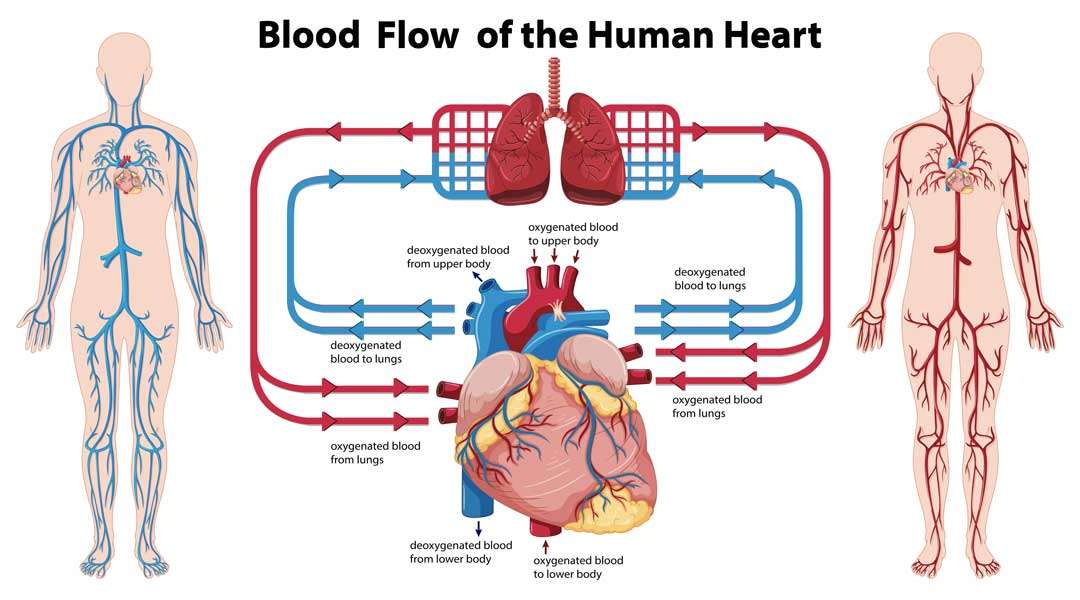
The main coronary artery is divided into two branches: left and right. Arteries transport oxygenated blood from the heart’s left ventricle to the body’s tissues and organs.
The heart not only does blood transport oxygen and nutrients to cells, but it also removes waste from those cells. Veins carry oxygen-depleted blood and waste products to the heart’s right side
The heart then sends blood to the lungs, where it is oxygenated, and carbon dioxide is expelled. After being re-pumped throughout the body, blood returns to the left side of the heart via the pulmonary veins. The kidneys and liver are in charge of removing most metabolic waste produced by cells.
Why heart failure happens?
Several factors can cause heart failure. Because of:
- A heart attack
- As a result, your heart muscle pumps inefficiently, which causes two issues:
- High blood pressure that lasts for a long time
- A faulty valve in your heart is possible.
- It’s possible that your excessive alcohol consumption evolved.
- The congenital disability
Symptoms of heart failure

What signs should you look for if you think you have heart failure? The heart failure brochure mentions the signs and symptoms including Shortness of breath with or without exertion and swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen are common warnings signs.
Additional warning signs of heart failure
Fatigue, weakness, feeling weaker or more exhausted than usual during routine activity, cold extremities, A sudden loss of appetite or feeling full, a dry, hacking cough, difficulty sleeping or staying asleep, waking up short of breath, and a sense of suffocation while lying down. Chest pain, an elevated heart rate, or an irregular heartbeat. These symptoms could be a combination or none at all.

Lifestyle Modifications as a Heart Failure Management Tool
You can lessen some heart failure symptoms and prevent them from getting worse by making changes to how you regularly go about your daily activities. Making progress towards a better way of life can help you live each day to the fullest, even though it may be difficult to break old habits. You may improve your ability to care for your physical and emotional health by becoming more self-aware and using the following tips.
Maintaining Control of Your Weight
Overweight can increases the peril of high blood pressure, stroke, heart disease, and diabetes because it puts more strain on the heart, which has to work harder to pump blood all over the body. Decrease the quantity of food you consume at each meal and your intake of high-calorie foods, fats, and sugars.
Here are some guidelines for keeping an eye on your weight:
- Weigh yourself every day at the same time;
- Keep a weight diary and track changes over a week;
- Alert your doctor if you notice any unexpected weight gain; (this may be caused by fluid retention and can increase the strain on your heart)
- Maintain a weight journal and track changes daily and week to week.
- Continue asking your doctor about a diuretic (water pill) action plan.

Don’t smoke
Quitters are much more likely to see a decrease in the severity of their heart failure symptoms. When you smoke, there is a chance that your heart and lungs will suffer harm.
Cut back on your alcohol consumption.
Alcohol abuse can worsen the symptoms of heart failure while also being bad for your heart. Because of this, your heart must exert more effort to pump blood throughout your body. If you consume alcohol, you should keep your intake to no more than two drinks for men and one for women daily.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications
Certain over-the-counter medications (medications that can purchase without a prescription from a doctor) have the potential to make heart failure symptoms worse. Consult your primary care physician or a pharmacist about the following before taking any over-the-counter medications: antacids, sodium-based cold medicines, herbal supplements, and vitamins.
- Painkillers, which may lead to increased salt retention in the kidneys.
- Products laced with ephedrine or ephedra.
Heart failure self care
In general, you should take various medications, eat a low-salt diet, drink fewer fluids, get enough rest, and occasionally engage in physical activity. Set the treatment goals include:
Improve heart health, reduce the effects of symptoms, and make every effort to avoid being readmitted to hospitals. Improve your chances of survival, enhance the overall quality of life.
Reduce the amount of salt you eat (Sodium).
Chronic heart failure patients must follow a low-salt diet. You should limit your sodium intake because sodium is the cause of water retention in the body, which can lead to edema and strain your heart. You can intake a maximum of 2 grams of sodium per day. How can you reduce the amount of salt you eat is as follows:
Remove the salt shaker from the table and stop using it immediately. Place it away. Avoid adding salt to the dish while it is being prepared. Pay close attention to the amount of salt listed on food labels when reading them.
Cut out processed foods high in sodium from your diet. The majority of sodium in the average diet comes from processed foods, containing up to 80% of their sodium from salt and other sodium-containing ingredients. Awareness of “hidden” salt sources is critical. For example, one slice of bread contains only 150 mg of sodium, but depending on how much bread is consumed daily, the total amount of salt consumed daily can be significant.
Most processed foods contain sodium, such as canned vegetables and frozen meals. Additional foods and condiments that contain a significant amount of salt include cheese, ketchup, lunch meat, pickles, and barbecue sauce. Consume more fruits and vegetables while they are still fresh. Consume meals low in salt, such as unsalted popcorn.
Use Potassium in food:
Patients with hypertension taking diuretics can require a higher daily intake of the mineral potassium. Contact your doctor if you suspect you require more potassium. Potassium can be found in a wide variety of foods, including chicken, fish, oranges and their juices, bananas, dates, raisins, mushrooms, potatoes, spinach, squash, and tomatoes, to name just a few.
Utilization of liquids.
You need to cut back on the fluids you consume since the more blood circulates through your body, the more work your heart has to do. Individuals who suffer from heart failure are forced to perform additional activities that place additional stress on their hearts.
It is mandatory to keep track of the amount of fluid you consume, particularly if you are using diuretics. Maintaining an appropriate hydration intake that is reasonable and sufficient is essential. You should discuss the amount and types of fluids you should consume with your attending physician or registered nurse.
It is recommended that individuals with heart failure limit the number of liquids they consume each day to between 6 and 8 cups (1500–2000 ml). Always keep track of the amount of water you drink when taking your prescription. Try chewing gum if you haven’t had many fluids to drink and your mouth feels dry. You can moisten your tongue by sipping water or sucking on hard candies. Both of these options are available to you.
Relaxation, movement, and physical activity
Your heart and your general health will both benefit from engaging in physical activity. Participating in consistent physical activity will enable you to progressively improve your strength while preventing your heart from being overworked.
You will be able to perform better on a day-to-day basis, enhance your muscle tone and strength, and experience fewer symptoms of chronic heart failure if you engage in regular exercise (such as shortness of breath and fatigue)
Physical activity does not need to be challenging for it to be effective. (In all seriousness, you should avoid physically taxing tasks.) Before commencing any exercise routine, make sure that you.
- Discuss it with the nurse or doctor at your Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) clinic and agree on feasible goals.
- Plan to get your workout done first thing in the morning or right after you wake up from an afternoon nap when you will have the most energy.
- Do sitting activities such as stretching whenever you get the opportunity.
- Interrupt your activity more frequently. Consider doing a series of shorter workouts more frequently throughout the day, depending on your energy. You could go for a walk that lasts ten minutes in the morning, stretch for ten minutes in the afternoon, and then go for a walk that lasts ten minutes in the evening. Stretching exercises are those that work out the muscles of the body.
After putting your head to one side and holding it there for ten seconds, swivel your head to the opposite side and straighten your neck again. Continue in this manner three times on each side.
While seated in a chair, bring the blades of your shoulders together and slowly raise them so that they are above your ears. After a delay, you should cast them aside once more. Repeat between 5 and 10 times.
Raise both arms out to the side until they are at shoulder height. It will constitute a shoulder circle. Ten times rotate the arms forward and backward in tight circles.
Heart Failure Drugs
Medication is an important part of your heart failure treatment. Medication has been shown in studies to improve health, prolong life, and delay disease progression. Even if you start to feel better, always take your medications as prescribed. Inform your doctor and pharmacist if you have any adverse reactions to medications. The medications listed below may be used to treat heart failure.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers lower blood pressure and make it easier for the heart to pump blood (ARBs).
Diuretics, also known as “water pills,” aid the kidneys and urine in excreting more water and salt, reducing swelling and shortness of breath.
Aldosterone inhibitors: They reduce the body’s water and salt content while also preventing heart muscle hardening and deterioration.
Beta-blockers: Lower blood pressure, improve heart rhythm, and strengthen the heart. They also reduce heart rate.
Vasodilators: These medications reduce blood vessel tension, reducing the workload on the heart.
Inotropic medications help to improve cardiac pumping.
ARNIs (Angiotensin-Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitors): This medication is a mix of two different medications. It reduces blood pressure, lowers blood pressure, and relaxes blood vessels.
Inhibitor: Reduces the workload on the heart by lowering the heart rate.
Inhibitors of SGLT2: This medication is used to treat both heart failure and diabetes. It may help to reduce the likelihood of hospitalization and death.
Other Treatments for Heart Disease
A pacemaker, defibrillator, or other specialized equipment is only used on rare occasions. People suffering from severe heart failure may have options such as (LVAD) or a heart transplant.